Financial Stability Board releases report on Financial Stability Implications of Multifunction Crypto-asset Intermediaries. Tokens (remember all those GME crypto tokens?) called out as interconnected-contagion risk!




Wut Mean?:
- MCIs generate revenue through proprietary trading and investments, including in self-issued crypto-assets.
- They often operate from offshore financial centers, are privately owned, and lack transparency in corporate structure, financial accounts, and product/service descriptions.
- In some cases, this opacity seems intentional, hindering understanding of their activities and risks.
- Typically, MCIs are controlled by a single individual or a small group, who retain decision-making authority.
- MCIs face vulnerabilities similar to traditional finance, like leverage and liquidity mismatch.
- These vulnerabilities can be amplified by MCIs' engagement in activities like proprietary trading, market making on their own platforms, and crypto-asset lending/borrowing, leading to higher leverage...
- MCIs' central role in the crypto-ecosystem and their market dominance add unique vulnerabilities.
- Their interconnectedness with the traditional financial system could cause spillover effects.
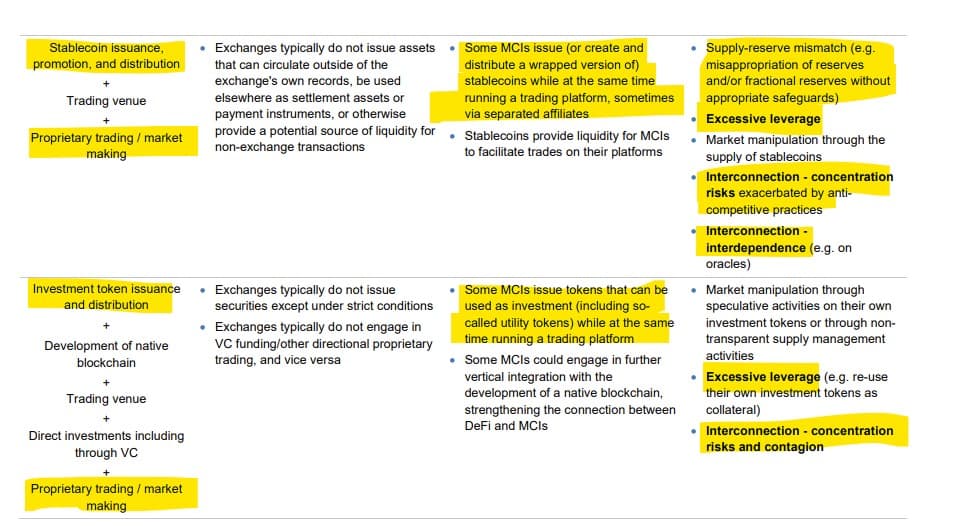
- MCIs are connected to financial institutions through service dependencies, direct exposures, or through stablecoins backed by traditional financial assets.
- The failure of a major MCI or a stablecoin they issue or promote could significantly impact crypto markets and cause broader economic spillovers.
- At present, the risk of an MCI failure threatening financial stability or the real economy seems limited, but the report calls out significant information gaps hinder a comprehensive assessment.
Substantial information gaps remain:
MCIs typically do not provide accurate and complete public disclosures, unlike traditional firms, due to the lack of or non-compliance with regulatory reporting requirements. They often disclose minimal corporate structure and governance information; reliable and complete balance sheet and other financial information is typically not available; product and service descriptions are lacking in material details; and various dependencies, linkages, and common exposures within MCIs, between MCIs, and with the financial system are only partially revealed in publicly available information. This lack of information makes it difficult to fully assess vulnerabilities associated with MCIs.
Key Activities:
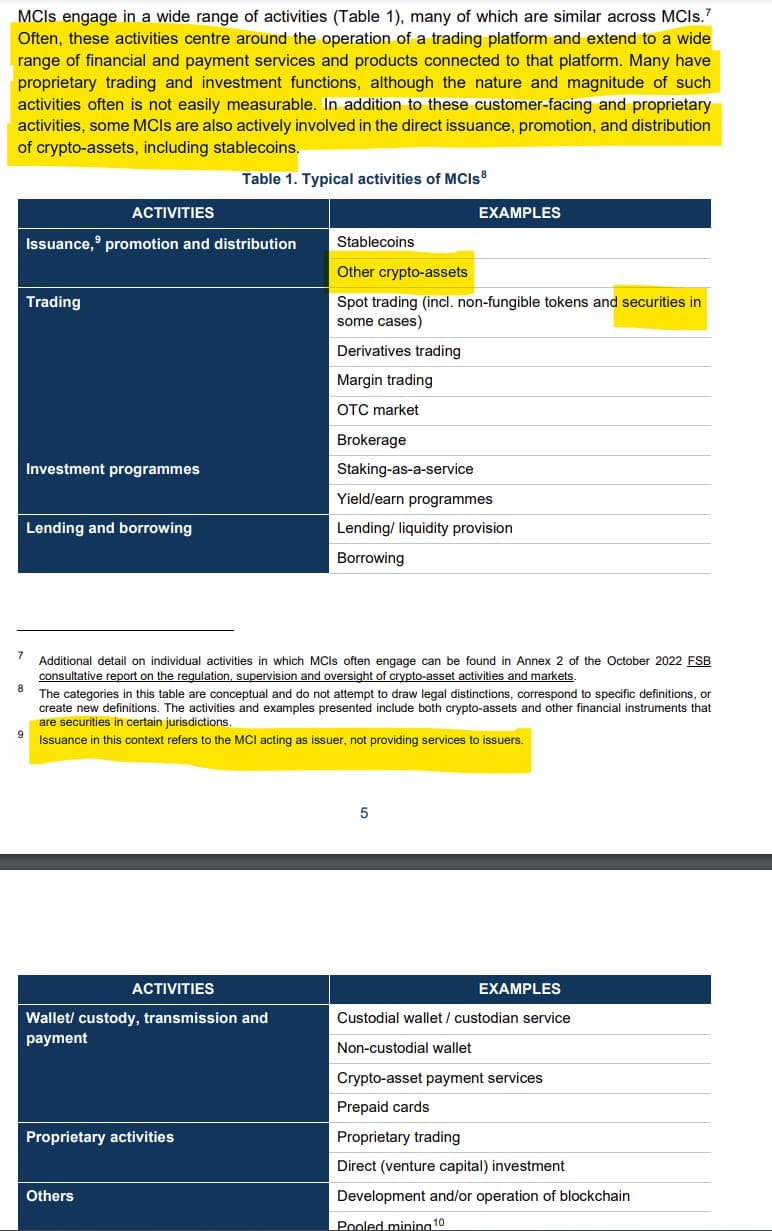
- For institutional clients, MCIs often offer a suite of prime brokerage services including over-the-counter (OTC) or “off-exchange” trading desks and market making, as well as access to liquidity for hedging, speculation, and working capital.
- In the course of offering these combined services to retail and institutional customers, MCIs may conduct much of the record-keeping and asset transfer on their own books and records.
- MCIs also conduct multiple proprietary trading and investment activities. MCIs often operate venture capital arms through which they finance crypto-asset-related projects and other start-ups. Some MCIs trade for themselves on their platforms in multiple capacities.
- Some of this trading activity can involve affiliates that engage in hedge fund-like trading strategies.
- Often, the existence and extent of this proprietary trading may not be disclosed to those who trade on MCIs.
Issuance, promotion, and distribution of crypto-assets:

Business model considerations and governance:

"The magnitude of these revenue sources is unclear given the limited information publicly disclosed, but it generally depends on the extent of trading activity on the MCI’s platform and the demand for crypto-assets more broadly."


"While spillovers to traditional finance so far have been limited, future stress events may reveal currently opaque interlinkages, in addition to the potential for these interlinkages to grow in connection with future developments."
Vulnerabilities of MCIs:

Leverage:

Liquidity Mismatch:

"Should the liquidity risk of the investments be poorly managed, the MCIs could fail to meet their obligations, such as sales, redemption, or withdrawal demands from their users."
Interconnections:

Amplifiers of MCI vulnerabilities:
Some MCIs may lack effective governance and risk management frameworks to manage the aforementioned vulnerabilities. MCI staff may lack experience and expertise in risk management and governance processes, exposing them and their clients to uncontrolled leverage and liquidity risks. Moreover, some MCIs may intentionally try to avoid regulatory oversight and/or operate in non-compliance with existing regulations, leading to no or little independent oversight of their risk management and governance frameworks by regulators. Poor risk management and the lack of governance and oversight may make it easier for insiders to engage in misconduct that magnifies MCI vulnerabilities. For example, a vulnerability can be exacerbated if governance controls are weak and part of the MCI is able to misappropriate assets or utilise commingled customer funds.
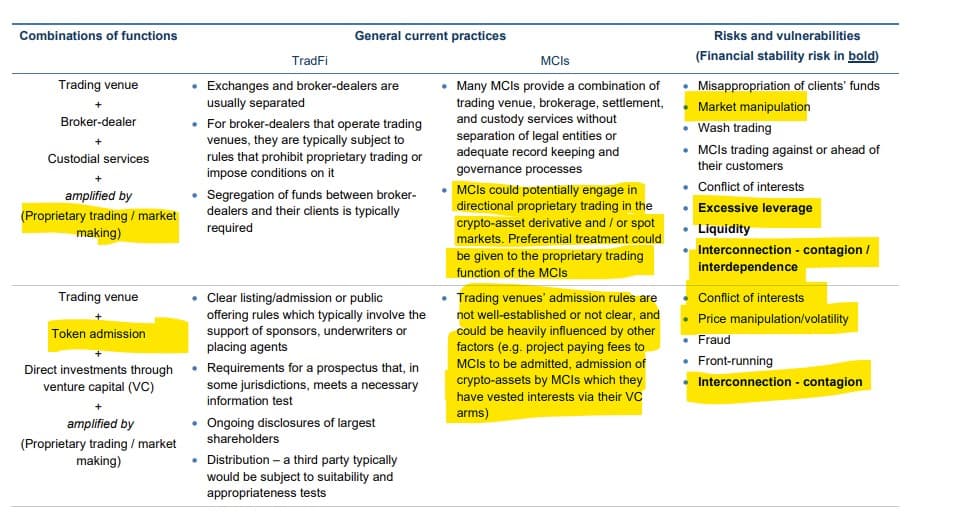
Conflicts of interest from the combination of certain functions amplify MCI vulnerabilities. In most jurisdictions, exchanges and broker-dealers are usually separated. Broker-dealers that operate trading venues are typically subject to rules that prohibit proprietary trading or impose other conditions. Segregation of funds between broker-dealers and their clients is required. MCIs are exposed to the amplified vulnerabilities when performing a combination of proprietary trading and market making on their own trading venues. They may have financial incentive and operational means to engage in market manipulation for assets they have issued, invested in, or accept as collateral. Another example of such manipulation is for MCIs to exaggerate the activity of trades on their own platforms.
In the absence of proper segregation safeguards, users’ funds and crypto-assets held by MCIs could potentially be misappropriated or re-hypothecated to invest into other crypto-asset related projects. This misuse would allow MCIs to take on further leverage and increase potential liquidity mismatch. Customers may not have their funds and crypto-assets returned to them on demand or may lose them permanently.
A lack of transparency and disclosure may prevent regulators or market participants from adequately assessing the safety and soundness of MCI business models. The lack of transparency and disclosure means that risks from, for example, the lack of effective governance and risk management, the lack of profitability of the business model, or weakness of the collateral supplied by borrowers, may be hidden until negative shocks materialise. This may also frustrate proper due diligence by market participants, for example investors in MCIs.
MCIs that operate on a global scale, while being headquartered or incorporated in lightly regulated jurisdictions or in jurisdictions with no applicable regulation, may complicate proper monitoring and enforcement of regulations by national authorities. As discussed in section 2.4, MCIs often provide services to users in jurisdictions in which the MCIs have no legal presence and/or appropriate licenses, or where the government may have restrictions or bans applicable to crypto-assets. While there were cases in the past in which some MCIs have voluntarily withdrawn their operations from individual jurisdictions, it is unclear if those MCIs have put in place robust on-boarding/know-your-customer procedures to identify and prevent users in those jurisdictions from accessing their platforms, even though some jurisdictions have warned MCIs against unregistered operations. The global reach of MCIs may also make it difficult to enforce existing regulation by some national authorities. The global and opaque structure of some MCIs may obscure vulnerabilities where neither regulators nor investors have a complete view into their activities and operations.
"In the absence of proper segregation safeguards, users’ funds and crypto-assets held by MCIs could potentially be misappropriated or re-hypothecated to invest into other crypto-asset related projects."
Financial stability interlinkages and transmission channels:


Risks and vulnerabilities associated with the combination of functions in MCIs:
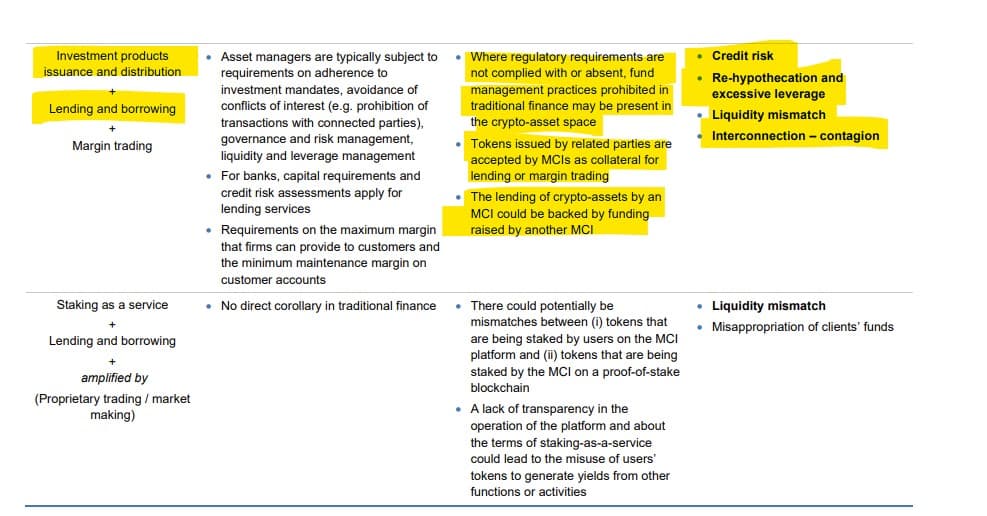
"Where regulatory requirements are not complied with or absent, fund management practices prohibited in traditional finance may be present in the crypto-asset space"
With that whopper of a statement, let's review what is known about GME tokens:



Remember, "Where regulatory requirements are not complied with or absent, fund management practices prohibited in traditional finance may be present in the crypto-asset space"...

TLDRS:
- Multifunction crypto-asset intermediaries (MCIs) generate revenue mainly through proprietary trading and investments, including in cryptocurrencies they issue themselves.
- MCIs often operate from offshore financial centers and are characterized by private ownership and a lack of transparency in their corporate structure, financials, and product descriptions, sometimes intentionally obscuring their activities and associated risks.
- Control of MCIs typically resides with a single individual or a small group, centralizing decision-making authority.
- These intermediaries are subject to vulnerabilities common in traditional finance, such as leverage and liquidity mismatch, which may be exacerbated by their involvement in proprietary trading, market making, and crypto-asset lending/borrowing.
- MCIs' key role in the crypto-ecosystem and their links with traditional financial institutions, including through stablecoins, create unique vulnerabilities and potential for significant spillovers to crypto markets and the broader economy, although current risks to financial stability are considered limited the report calls out lack of information makes it impossible to tell for sure what it going on.
- The report says the quiet part out loud: "Where regulatory requirements are not complied with or absent, fund management practices prohibited in traditional finance may be present in the crypto-asset space"
- It sure seems all this opaqueness is what attracted Ken Griffin to Silvergate, which was then all up in FTX's business?



