Federal Reserve Alert! 109th Annual Report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System to Congress: "Based on a number of measures, leverage at hedge funds during 2022 stood above its historical average." Hedgies R Fukt!

https://www.federalreserve.gov/publications/files/2022-annual-report.pdf
This report covers the calendar-year operations and activities carried out by the Board in its five key functional areas: (1) monetary policy, (2) financial stability, (3) supervision and regulation, (4) payment system and Reserve Bank oversight, and (5) consumer and community affairs.
The appendix of this report contains additional information on Federal Reserve leadership, policy actions, budgets, updated historical data, and other supporting activities.

Highlights:Asset Valuation Pressures
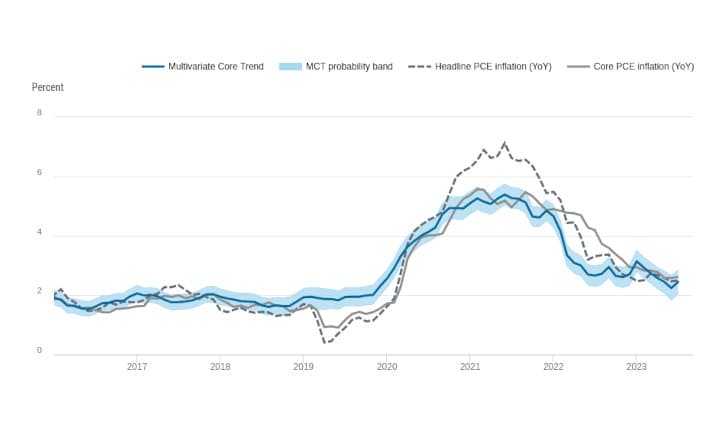
In 2022, we saw high inflation and a tight labor market. This led to tighter monetary policy and a worsening economic outlook. Long-term Treasury yields rose significantly, which, along with a reduced appetite for risk, led to a decline in broad equity indexes and a widening of corporate credit spreads. The valuation measures for most corporate financial assets moved closer to their historical averages. However, real estate valuations remained high.
Specifically, the prices of long-term Treasury securities and leveraged loans fell over the year, leading to higher yields. Corporate bond yield spreads over comparable-maturity Treasury yields widened in the first half of 2022 but slightly narrowed toward the end of the year, indicating a return of risk appetite, especially for speculative-grade corporate bonds. Equity prices fell due to uncertainty about the economic outlook, and the ratio of equity prices to expected earnings, a key indicator of equity valuations, declined to near its historical median. The volatility index (VIX) for the S&P 500 index remained high throughout the year, reflecting market uncertainty.
Rising borrowing costs and tighter lending standards put downward pressure on home values, with various house price indexes showing small price declines since last summer. However, valuation pressures in the residential real estate sector remained high by historical standards, with the price-to-rent ratio remaining at the upper end of its historical distribution due to a tight inventory of homes for sale.
Commercial real estate (CRE) prices remained high by historical standards, but there were signs of easing valuation pressures in the CRE sector.
Borrowing by Households:

Credit card and auto delinquency rates for near-prime and subprime borrowers increased significantly. Student loan delinquencies were held down by the extension of the repayment holiday.
Leverage:

hedgies r fuk
Funding Risk:

- A measure of banks' exposure to interest rate risk, calculated as the difference between the effective time to maturity (or next contractual interest rate adjustment) for bank assets and liabilities, decreased slightly in the second half of the year. However, it remained near the top of its historical range. This means banks are still relatively exposed to the risk of interest rate changes.
MMFs and similar cash-management vehicles remain a prominent source of vulnerability:
In 2022, assets under management (AUM) of money market funds (MMFs), which are investment vehicles that invest in short-term debt securities, grew rapidly.
- This growth, particularly in prime MMFs, likely reflects their yields increasing faster than the yields of other MMFs and deposit rates, as short-term interest rates have risen.
- The combined AUM in other cash-management vehicles—such as offshore prime MMFs, short-term investment funds, private liquidity funds, and ultrashort bond funds—also continued to increase and remained high by historical standards.
- However, these funds are susceptible to runs (when many investors withdraw their money at the same time), and they play a significant role in short-term funding markets. Therefore, MMFs and similar cash-management vehicles remain a prominent source of vulnerability in the financial system.

In 2022, the Federal Reserve completed 41 formal enforcement actions. Civil money penalties totaling $30,450,400 were assessed.