FDIC Alert! Notice of Designated Reserve Ratio for 2024. FDIC designates that the Designated Reserve Ratio (DRR) for the Deposit Insurance Fund shall remain at 2 percent for 2024.


What is the Designated Reserve Ratio?
- The Federal Deposit Insurance Act requires the FDIC's Board of Directors to set a target or Designated Reserve Ratio (DRR) for the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) annually.
- The DRR is the total of the DIF divided by the total estimated insured deposits of the industry. Under the long-range plan, the FDIC set the DRR at 2.0 percent and set a schedule of assessment rates that would progressively decrease when the Fund Management exceeds 2.0 percent and 2.5 percent.
- Since 2010, the Board as adopted a 2.0 percent DRR each year.
- An analysis using historical fund loss and simulated income data from 1950 to 2010 showed that the DRR would had to have exceeded 2.0 percent before the onset of the two crises that occurred during the past 30 years to have maintained both a positive fund balance and stable assessment rates throughout both crises.
- The FDIC views the 2.0 percent DRR as a long-term goal and the minimum level needed to withstand future crises of the magnitude of past crises.
- Dodd-Frank set the required minimum reserve ratio to 1.35 percent.
- If the reserve ratio falls below 1.35 percent or is expected to within 6 months, the FDIC generally must adopt a restoration plan to restore the DIF reserve ratio to at least 1.35 percent within 8 years.
- There is no upper limit on the reserve ratio and thus, no statutory limit on the size of the fund.
- The FDI Act provides for dividends from the fund when the reserve ratio exceeds 1.5 percent, but grants the Board sole discretion in determining whether to suspend or limit the declaration or payment of dividends.
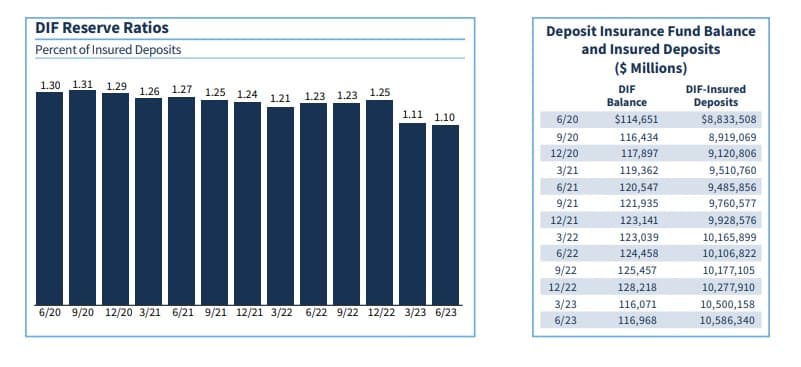
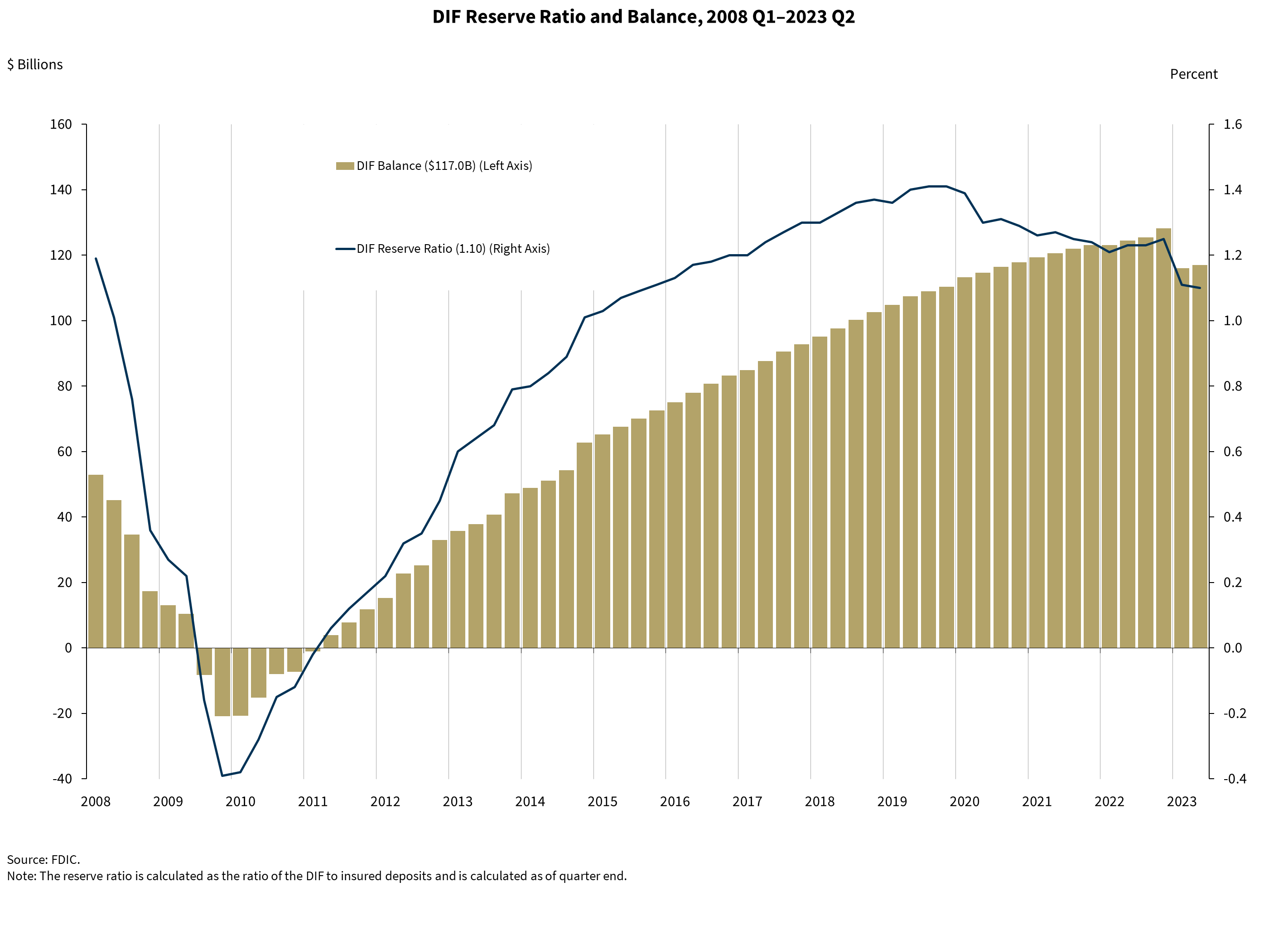
- During the second quarter, the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) balance increased by $897 million to $117.0 billion.
- The rise in the DIF was primarily driven by assessment income of $3.1 billion.
- The FDIC recognized a substantial portion of the estimated loss to the Fund associated with First Republic Bank as part of the $16.4 billion in loss provisions recorded for first quarter 2023.
- As a result, the $2.0 billion in loss provisions recorded for second quarter 2023 is considerably below the expected loss for that institution.
- The DIF’s reserve ratio (the fund balance as a percent of insured deposits) was 1.10 percent on June 30, 2023, down 1 basis point from the previous quarter and 13 basis points lower than the previous year.
The Board must set the DRR in accordance with its analysis of the following statutory factors:
- Risk of losses to the DIF;
- Economic conditions generally affecting insured depository institutions;
- Preventing sharp swings in assessment rates; and
- Any other factors that the Board determines to be appropriate.

TLDRS:
- FDIC designates that the Designated Reserve Ratio (DRR) for the Deposit Insurance Fund shall remain at 2 percent for 2024.
- Since 2010, the DRR has been set at 2.0 percent. Historical data suggests a DRR above 2.0 percent is needed to maintain stability in crises.
- Dodd-Frank mandates a minimum reserve ratio of 1.35 percent, with no upper limit set for the reserve ratio.
- If the reserve ratio falls below 1.35 percent (at 1.10 percent as of 6/30/23) or is expected to within 6 months, the FDIC must adopt a restoration plan to reach at least 1.35 percent within 8 years.
- With 5 bank failure so far this year (with assets greater than 2008-2009 combined), it would seem the status quo is the wrong move, especially since DIF is well below the 1.35 percent mandated by Dodd-Frank.
- Is this a backhanded attempt at a public bailout since the DIF is not properly funded?